At the time of the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962, the United States had decisive nuclear superiority over the Soviet Union. This country had more than 400 Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) compared to 78 ICBMs in the Soviet arsenal. The huge strategic advantage also included the sophisticated Polaris submarines with a devastating nuclear punch and the overwhelming striking power of some 1,300 bombers with nuclear ordinance, as opposed to less than 200 belonging to the Soviets.
Moreover, in the early 1960’s the delivery time from the launching site to the target was a crucial factor. It took approximately 30 minutes for the Soviet missiles to reach the United States. This was enough time for the Americans to retaliate with a devastating counter-strike, which was an essential deterrence for peace. From Cuba, the Soviet missiles would have been able to destroy most of the U.S. military and urban centers in 7-10 minutes.
Another important factor was that the missile accuracy significantly increased with the proximity of the target, making the Marxist island of Cuba the perfect choice to greatly improve Soviet nuclear capacity.
Yuri Pavlov, former head of the Soviet Latin America’s Foreign Ministry and responsible for Soviet-Cuban relations, wrote in 1994: “The Soviet leadership decided to use the island in order to bring a substantial part of the United States territory within range of Soviet medium range ballistic missiles armed with nuclear warheads. Khrushchev, who initiated this idea, hoped that it would help to address the imbalance (in) strategic nuclear force.”

Anatoly Dobrynin and JFK.
Anatoly Dobrynin, Soviet ambassador to Washington and a decisive figure with Robert Kennedy in finding a solution to the crisis, stated, in his memoirs published in 1995, that Khrushchev’s motives for the missiles deployment in Cuba was strategic. He wrote: “The move was part of a broader geopolitical strategy to achieve greater parity with the United States.”
A principal factor in the Kremlin’s decision to introduce nuclear missiles into Cuba was the Bay of Pigs disaster, where John Kennedy was perceived as a weak, indecisive president who would cave in under pressure. The next move was to get Fidel Castro’s cooperation. The messenger was Ambassador Aleksandr Alexeyev, a veteran KGB agent and close associate of Raúl Castro.
Fidel Castro welcomed the idea of nuclear missiles in Cuba. In his meeting with Aleksandr, the Marxist dictator stated: “That is a very risky move . . . but if making such a decision is indispensable for the Socialist bloc, I think I am in favor of placing the missiles in our island. This way we will be able to be the first victims of the encounter against imperialism.” With Castro’s endorsement, the secret shipment and deployment was on.
But on October 14, a U.S. aircraft (U-2) took photos that provided Washington with the first hard evidence of the Soviet missiles in Cuba. Two days later, President Kennedy was informed. For the next five days, in absolute secrecy, the president and close advisors analyzed the available options. At the end, it was decided to confront, head-on, the Soviet challenge.
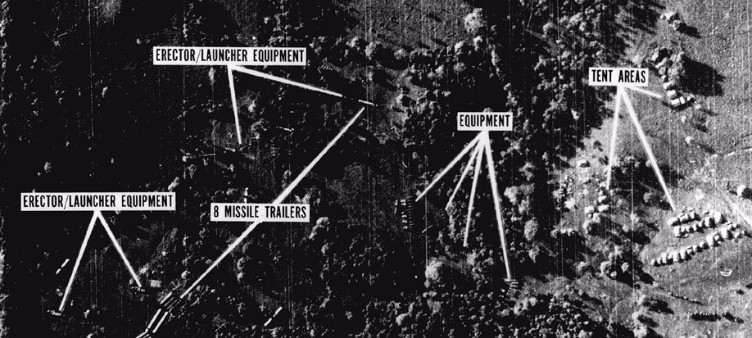
MRBM Field Launch Site in San Cristobal, Cuba. October, 1962.
On October 22, at 7 p.m., President Kennedy addressed the nation in a televised speech disclosing that Soviet nuclear missiles were in Cuba, announcing a strict quarantine of all offensive weapons being shipped to the island and warning Moscow that if they were not immediately withdrawn, the United States was ready to remove them by force.
Dobrynin knew that the Kremlin was caught empty handed by the forceful American reaction.
In his memoirs he said, “The fatal miscalculation was made by Khrushchev himself. He did not anticipate that his adventurous thrust would be discovered in time for Kennedy to organize a sharp reaction, including a direct confrontation.”
It was in this critical moment that Fidel Castro’s apocalyptic behavior became evident. He wrote to Khrushchev, calling on the Soviets to launch a pre-emptive nuclear attack against the United States.

On October 27, a U-2 plane was shot down over the island and its pilot killed. The U.S. military began the final stage of a massive deployment for the attack on Castro’s Cuba. Late that night, Robert Kennedy met with Dobrynin and went straight to the point. The president demanded the immediate withdrawal of the missiles from Cuba. Otherwise the United States would do it by force.
At 4 p.m. on Sunday, October 28, the Soviet leadership sent an urgent message to Dobrynin in Washington indicating that Khrushchev had accepted the president’s demands. To avoid any delays, the news was broadcasted on Radio Moscow. The agreement also included a secret covenant for the gradual dismantling of the obsolete American missiles in Turkey and a pledge not to invade Cuba. During the negotiations, Castro was ignored and consequently felt humiliated.
But who won? Kennedy was murdered a year later by a pro-Castro assassin. Khrushchev was sacked as prime minister within two years and Castro remained as Cuba’s bloody tyrant until his death in 2016. You decide.
Transcript of John F. Kennedy’s Address to the Nation on the Cuban Missile Crisis, 1962

«Good evening, my fellow citizens:
This Government, as promised, has maintained the closest surveillance of the Soviet military buildup on the island of Cuba. Within the past week, unmistakable evidence has established the fact that a series of offensive missile sites is now in preparation on that imprisoned island. The purpose of these bases can be none other than to provide a nuclear strike capability against the Western Hemisphere.
Upon receiving the first preliminary hard information of this nature last Tuesday morning at 9 A.M., I directed that our surveillance be stepped up. And having now confirmed and completed our evaluation of the evidence and our decision on a course of action, this Government feels obliged to report this new crisis to you in fullest detail.
The characteristics of these new missile sites indicate two distinct types of installations. Several of them include medium range ballistic missiles, capable of carrying a nuclear warhead for a distance of more than 1,000 nautical miles. Each of these missiles, in short, is capable of striking Washington, D. C., the Panama Canal, Cape Canaveral, Mexico City, or any other city in the southeastern part of the United States, in Central America, or in the Caribbean area.
Additional sites not yet completed appear to be designed for intermediate range ballistic missiles — capable of traveling more than twice as far — and thus capable of striking most of the major cities in the Western Hemisphere, ranging as far north as Hudson Bay, Canada, and as far south as Lima, Peru. In addition, jet bombers, capable of carrying nuclear weapons, are now being uncrated and assembled in Cuba, while the necessary air bases are being prepared.
This urgent transformation of Cuba into an important strategic base — by the presence of these large, long-range, and clearly offensive weapons of sudden mass destruction — constitutes an explicit threat to the peace and security of all the Americas, in flagrant and deliberate defiance of the Rio Pact of 1947, the traditions of this nation and hemisphere, the joint resolution of the 87th Congress, the Charter of the United Nations, and my own public warnings to the Soviets on September 4 and 13. This action also contradicts the repeated assurances of Soviet spokesmen, both publicly and privately delivered, that the arms buildup in Cuba would retain its original defensive character, and that the Soviet Union had no need or desire to station strategic missiles. on the territory of any other nation.
The size of this undertaking makes clear that it has been planned for some months. Yet, only last month, after I had made clear the distinction between any introduction of ground-to-ground missiles and the existence of defensive antiaircraft missiles, the Soviet Government publicly stated on September 11 that, and I quote, “the armaments and military equipment sent to Cuba are designed exclusively for defensive purposes,” that there is, and I quote the Soviet Government, “there is no need for the Soviet Government to shift its weapons for a retaliatory blow to any other country, for instance Cuba,” and that, and I quote their government, “the Soviet Union has so powerful rockets to carry these nuclear warheads that there is no need to search for sites for them beyond the boundaries of the Soviet Union.”
That statement was false.
Only last Thursday, as evidence of this rapid offensive buildup was already in my hand, Soviet Foreign Minister Gromyko told me in my office that he was instructed to make it clear once again, as he said his government had already done, that Soviet assistance to Cuba, and I quote, “pursued solely the purpose of contributing to the defense capabilities of Cuba,” that, and I quote him, “training by Soviet specialists of Cuban nationals in handling defensive armaments was by no means offensive, and if it were otherwise,” Mr. Gromyko went on, “the Soviet Government would never become involved in rendering such assistance.”
That statement also was false.
Neither the United States of America nor the world community of nations can tolerate deliberate deception and offensive threats on the part of any nation, large or small. We no longer live in a world where only the actual firing of weapons represents a sufficient challenge to a nation’s security to constitute maximum peril. Nuclear weapons are so destructive and ballistic missiles are so swift, that any substantially increased possibility of their use or any sudden change in their deployment may well be regarded as a definite threat to peace.
For many years, both the Soviet Union and the United States, recognizing this fact, have deployed strategic nuclear weapons with great care, never upsetting the precarious status quo which insured that these weapons would not be used in the absence of some vital challenge. Our own strategic missiles have never been transferred to the territory of any other nation under a cloak of secrecy and deception; and our history — unlike that of the Soviets since the end of World War II — demonstrates that we have no desire to dominate or conquer any other nation or impose our system upon its people. Nevertheless, American citizens have become adjusted to living daily on the bull’s-eye of Soviet missiles located inside the U.S.S.R. or in submarines.
In that sense, missiles in Cuba add to an already clear and present danger — although it should be noted the nations of Latin America have never previously been subjected to a potential nuclear threat. But this secret, swift, extraordinary buildup of Communist missiles — in an area well known to have a special and historical relationship to the United States and the nations of the Western Hemisphere, in violation of Soviet assurances, and in defiance of American and hemispheric policy — this sudden, clandestine decision to station strategic weapons for the first time outside of Soviet soil — is a deliberately provocative and unjustified change in the status quo which cannot be accepted by this country, if our courage and our commitments are ever to be trusted again by either friend or foe.
The 1930’s taught us a clear lesson: aggressive conduct, if allowed to go unchecked and unchallenged, ultimately leads to war. This nation is opposed to war. We are also true to our word. Our unswerving objective, therefore, must be to prevent the use of these missiles against this or any other country, and to secure their withdrawal or elimination from the Western Hemisphere.
Our policy has been one of patience and restraint, as befits a peaceful and powerful nation which leads a worldwide alliance. We have been determined not to be diverted from our central concerns by mere irritants and fanatics. But now further action is required, and it is under way; and these actions may only be the beginning. We will not prematurely or unnecessarily risk the costs of worldwide nuclear war in which even the fruits of victory would be ashes in our mouth; but neither will we shrink from that risk at any time it must be faced.
Acting, therefore, in the defense of our own security and of the entire Western Hemisphere, and under the authority entrusted to me by the Constitution as endorsed by the Resolution of the Congress, I have directed that the following initial steps be taken immediately:
First: To halt this offensive buildup a strict quarantine on all offensive military equipment under shipment to Cuba is being initiated. All ships of any kind bound for Cuba from whatever nation or port will, if found to contain cargoes of offensive weapons, be turned back. This quarantine will be extended, if needed, to other types of cargo and carriers. We are not at this time, however, denying the necessities of life as the Soviets attempted to do in their Berlin blockade of 1948.
Second: I have directed the continued and increased close surveillance of Cuba and its military buildup. The foreign ministers of the OAS [Organization of American States], in their communiqué’ of October 6, rejected secrecy on such matters in this hemisphere. Should these offensive military preparations continue, thus increasing the threat to the hemisphere, further action will be justified. I have directed the Armed Forces to prepare for any eventualities; and I trust that in the interest of both the Cuban people and the Soviet technicians at the sites, the hazards to all concerned of continuing this threat will be recognized.
Third: It shall be the policy of this nation to regard any nuclear missile launched from Cuba against any nation in the Western Hemisphere as an attack by the Soviet Union on the United States, requiring a full retaliatory response upon the Soviet Union.
Fourth: As a necessary military precaution, I have reinforced our base at Guantanamo, evacuated today the dependents of our personnel there, and ordered additional military units to be on a standby alert basis.
Fifth: We are calling tonight for an immediate meeting of the Organization of Consultation under the Organization of American States, to consider this threat to hemispheric security and to invoke articles 6 and 8 of the Rio Treaty in support of all necessary action. The United Nations Charter allows for regional security arrangements, and the nations of this hemisphere decided long ago against the military presence of outside powers. Our other allies around the world have also been alerted.
Sixth: Under the Charter of the United Nations, we are asking tonight that an emergency meeting of the Security Council be convoked without delay to take action against this latest Soviet threat to world peace. Our resolution will call for the prompt dismantling and withdrawal of all offensive weapons in Cuba, under the supervision of U.N. observers, before the quarantine can be lifted.
Seventh and finally: I call upon Chairman Khrushchev to halt and eliminate this clandestine, reckless, and provocative threat to world peace and to stable relations between our two nations. I call upon him further to abandon this course of world domination, and to join in an historic effort to end the perilous arms race and to transform the history of man. He has an opportunity now to move the world back from the abyss of destruction by returning to his government’s own words that it had no need to station missiles outside its own territory, and withdrawing these weapons from Cuba by refraining from any action which will widen or deepen the present crisis, and then by participating in a search for peaceful and permanent solutions.
This nation is prepared to present its case against the Soviet threat to peace, and our own proposals for a peaceful world, at any time and in any forum — in the OAS, in the United Nations, or in any other meeting that could be useful — without limiting our freedom of action. We have in the past made strenuous efforts to limit the spread of nuclear weapons. We have proposed the elimination of all arms and military bases in a fair and effective disarmament treaty. We are prepared to discuss new proposals for the removal of tensions on both sides, including the possibilities of a genuinely independent Cuba, free to determine its own destiny. We have no wish to war with the Soviet Union — for we are a peaceful people who desire to live in peace with all other peoples.
But it is difficult to settle or even discuss these problems in an atmosphere of intimidation. That is why this latest Soviet threat — or any other threat which is made either independently or in response to our actions this week– must and will be met with determination. Any hostile move anywhere in the world against the safety and freedom of peoples to whom we are committed, including in particular the brave people of West Berlin, will be met by whatever action is needed.
Finally, I want to say a few words to the captive people of Cuba, to whom this speech is being directly carried by special radio facilities. I speak to you as a friend, as one who knows of your deep attachment to your fatherland, as one who shares your aspirations for liberty and justice for all. And I have watched and the American people have watched with deep sorrow how your nationalist revolution was betrayed — and how your fatherland fell under foreign domination. Now your leaders are no longer Cuban leaders inspired by Cuban ideals. They are puppets and agents of an international conspiracy which has turned Cuba against your friends and neighbors in the Americas, and turned it into the first Latin American country to become a target for nuclear war — the first Latin American country to have these weapons on its soil.
These new weapons are not in your interest. They contribute nothing to your peace and well-being. They can only undermine it. But this country has no wish to cause you to suffer or to impose any system upon you. We know that your lives and land are being used as pawns by those who deny your freedom. Many times, in the past, the Cuban people have risen to throw out tyrants who destroyed their liberty. And I have no doubt that most Cubans today look forward to the time when they will be truly free — free from foreign domination, free to choose their own leaders, free to select their own system, free to own their own land, free to speak and write and worship without fear or degradation. And then shall Cuba be welcomed back to the society of free nations and to the associations of this hemisphere.
My fellow citizens, let no one doubt that this is a difficult and dangerous effort on which we have set out. No one can foresee precisely what course it will take or what costs or casualties will be incurred. Many months of sacrifice and self-discipline lie ahead — months in which both our patience and our will be tested, months in which many threats and denunciations will keep us aware of our dangers. But the greatest danger of all would be to do nothing.
The path we have chosen for the present is full of hazards, as all paths are; but it is the one most consistent with our character and courage as a nation and our commitments around the world. The cost of freedom is always high, but Americans have always paid it. And one path we shall never choose, and that is the path of surrender or submission.
Our goal is not the victory of might, but the vindication of right; not peace at the expense of freedom, but both peace and freedom, here in this hemisphere, and, we hope, around the world. God willing, that goal will be achieved.
Thank you and good night.»









